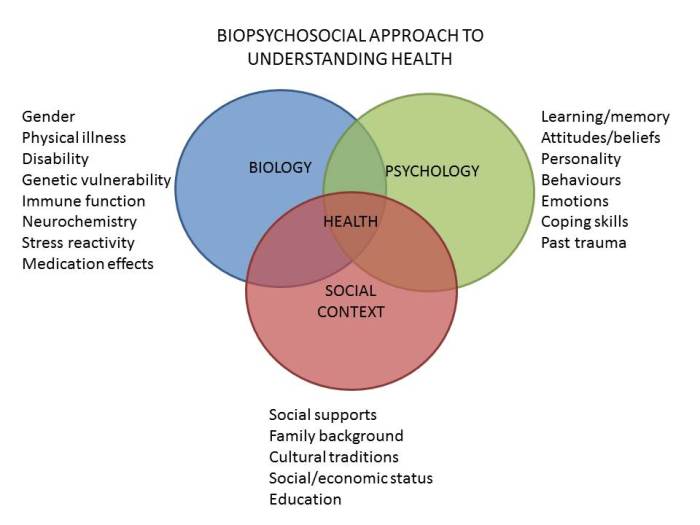
The controlling factor for the functionalist perspective is – The controlling factor, a linchpin of the functionalist perspective, plays a pivotal role in shaping the functioning of systems across diverse domains. This concept, with its multifaceted nature, serves as a guiding principle for understanding the intricate relationships within and between systems.
Its essential characteristics, types, and applications provide a comprehensive framework for analyzing and interpreting the behavior of complex systems, offering valuable insights into their structure, dynamics, and outcomes.
1. Definition and Overview of the Controlling Factor in the Functionalist Perspective
In the functionalist perspective, the controlling factor refers to the dominant or influential element that governs the functioning and behavior of a system. It acts as a central force that shapes the interactions and relationships within the system, influencing its overall structure, processes, and outcomes.
The controlling factor can manifest in various forms, such as a dominant institution, a set of norms or values, or a particular environmental constraint. It exerts its influence by guiding the allocation of resources, shaping decision-making processes, and establishing boundaries for acceptable behavior within the system.
2. Key Characteristics of the Controlling Factor, The controlling factor for the functionalist perspective is
The controlling factor in the functionalist perspective possesses several key characteristics:
- Dominant Influence:It holds a position of power or authority within the system, enabling it to exert significant influence over other elements.
- Systemic Scope:Its influence extends across the entire system, affecting the behavior of all its components and their interactions.
- Stability and Persistence:It tends to be relatively stable and enduring, providing a consistent framework for the system’s functioning.
- Functional Integration:It contributes to the overall functioning and integration of the system, ensuring its coherence and effectiveness.
3. Types and Classification of Controlling Factors
Controlling factors can be categorized into different types based on their nature, function, or domain:
- Institutional Controlling Factors:These are formal organizations or institutions that possess significant authority and influence within the system, such as governments, corporations, or religious institutions.
- Normative Controlling Factors:These are shared values, beliefs, or norms that guide the behavior of individuals and groups within the system, shaping their interactions and expectations.
- Environmental Controlling Factors:These are external constraints or influences that impact the system’s functioning, such as economic conditions, technological advancements, or physical environment.
4. Role of the Controlling Factor in Functionalist Analysis
The controlling factor plays a crucial role in functionalist analysis by:
- Identifying Patterns and Relationships:It helps identify patterns and relationships within the system, revealing how different elements interact and contribute to its overall functioning.
- Understanding System Dynamics:By analyzing the controlling factor, researchers can gain insights into the dynamics of the system, its stability, and potential for change.
- Predicting System Outcomes:Understanding the controlling factor allows for more accurate predictions about the system’s behavior and potential outcomes, enabling informed decision-making.
Essential Questionnaire: The Controlling Factor For The Functionalist Perspective Is
What is the fundamental concept behind the controlling factor in the functionalist perspective?
The controlling factor is a key element that exerts a dominant influence on the functioning and behavior of a system, shaping its structure, dynamics, and outcomes.
How does the controlling factor influence system behavior?
The controlling factor acts as a guiding force, directing the system’s activities towards specific goals or objectives, ensuring its stability and coherence.
What are the key characteristics of the controlling factor?
The controlling factor is typically characterized by its dominance, pervasiveness, and impact on the system’s overall functioning.
What are the different types of controlling factors?
Controlling factors can be classified based on their nature, function, or domain, including environmental factors, internal mechanisms, or cultural norms.
What is the role of the controlling factor in functionalist analysis?
The controlling factor provides a framework for understanding and analyzing systems, enabling researchers to identify patterns, relationships, and outcomes that shape system behavior.