Make an electron distribution diagram of water – Unveiling the molecular intricacies of water, this exploration delves into the realm of electron distribution diagrams, providing a comprehensive understanding of the arrangement and behavior of electrons within the H2O molecule. By unraveling the electronic structure, we embark on a journey to decipher the unique properties and characteristics that define water.
Through a systematic approach, we will delve into the electron configuration, Lewis structure, molecular geometry, polarity, and hydrogen bonding of water, shedding light on the fundamental principles that govern its chemical and physical behavior.
Electron Configuration of Water
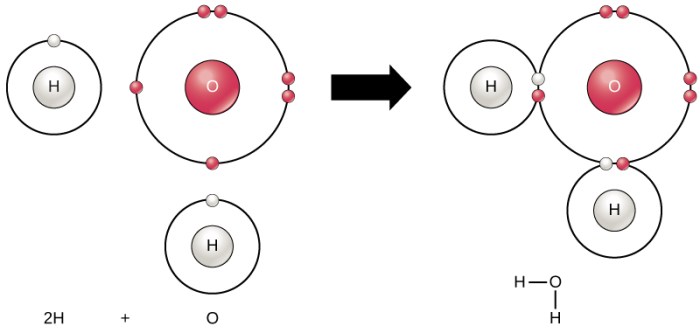
Water (H2O) is a polar molecule with a bent shape. The electron configuration of water can be represented as:
s22s 22p 6
This indicates that the oxygen atom in water has two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and six electrons in the 2p orbitals. The hydrogen atoms each have one electron in the 1s orbital.The electrons in the 2p orbitals of the oxygen atom are arranged in a tetrahedral shape.
Two of the p orbitals overlap with the s orbitals of the hydrogen atoms to form two covalent bonds. The other two p orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons.The lone pairs of electrons on the oxygen atom repel each other, causing the molecule to have a bent shape.
The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is approximately 104.5 degrees.
Lewis Structure of Water
The Lewis structure of water shows the arrangement of atoms and bonds in the molecule. The Lewis structure of water is:H:O:HThis indicates that the oxygen atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms by single bonds. The oxygen atom also has two lone pairs of electrons.The
Lewis structure of water can be used to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. The tetrahedral electron pair geometry of the oxygen atom indicates that the molecule will have a bent shape.
Molecular Geometry of Water
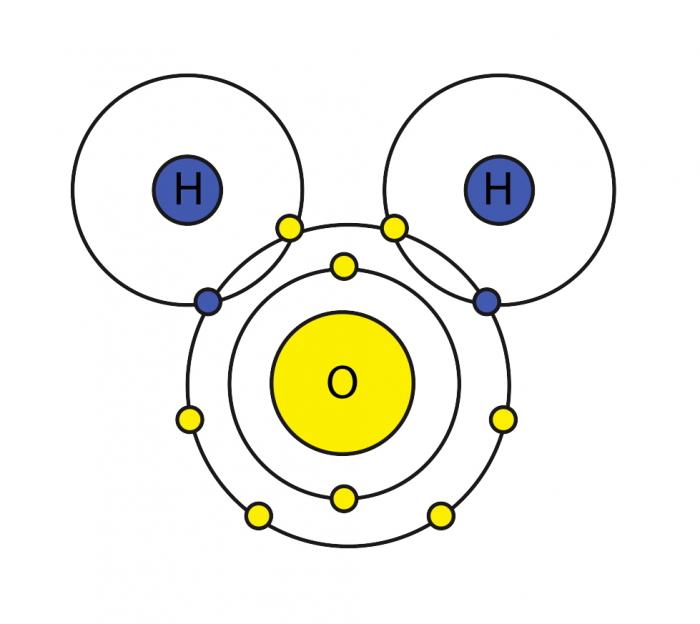
The molecular geometry of water is tetrahedral. This means that the oxygen atom is surrounded by four electron pairs, two of which are bonding pairs and two of which are lone pairs.The tetrahedral electron pair geometry results in a bent molecular shape.
The bond angle between the two hydrogen atoms is approximately 104.5 degrees.The molecular geometry of water has a significant impact on its properties. The bent shape of the molecule allows water to form hydrogen bonds with other water molecules. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for many of the unique properties of water, such as its high surface tension and its ability to dissolve many substances.
Polarity of Water
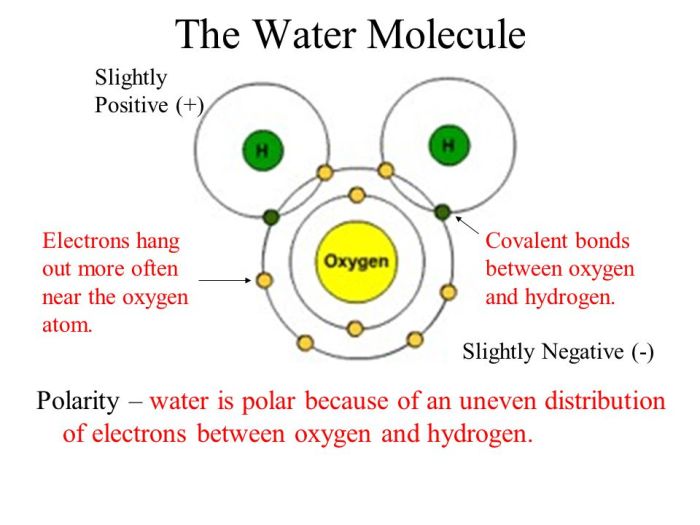
Water is a polar molecule. This means that it has a positive end and a negative end. The positive end of the molecule is the hydrogen atoms, and the negative end of the molecule is the oxygen atom.The polarity of water is due to the uneven distribution of electrons in the molecule.
The oxygen atom has a higher electronegativity than the hydrogen atoms, which means that it attracts electrons more strongly. This results in a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom and a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms.The polarity of water is important for many of its properties.
For example, the polarity of water allows it to dissolve many ionic compounds.
Hydrogen Bonding in Water
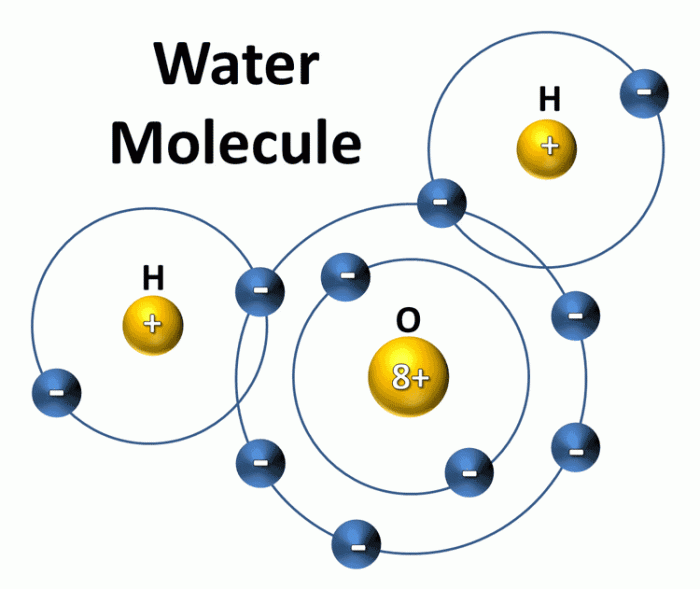
Hydrogen bonding is a type of intermolecular force that occurs between a hydrogen atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom.In water, hydrogen bonding occurs between the hydrogen atoms of one water molecule and the oxygen atom of another water molecule.
The hydrogen atom that is involved in hydrogen bonding is partially positive, and the oxygen atom that is involved in hydrogen bonding is partially negative. This allows the hydrogen atom to be attracted to the oxygen atom, forming a hydrogen bond.Hydrogen
bonding is responsible for many of the unique properties of water. For example, hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high surface tension of water and its ability to dissolve many substances.
FAQ: Make An Electron Distribution Diagram Of Water
What is the electron configuration of water?
The electron configuration of water (H2O) is 1s2 2s2 2p6, indicating two valence electrons in the outermost energy level.
How is the Lewis structure of water drawn?
The Lewis structure of water shows the arrangement of atoms and bonds, with two hydrogen atoms single-bonded to a central oxygen atom.
What is the molecular geometry of water?
Water has a tetrahedral electron pair geometry, resulting in a bent molecular shape with a bond angle of approximately 104.5 degrees.
Is water polar or nonpolar?
Water is a polar molecule due to the uneven distribution of electrons, resulting in a dipole moment and partial positive and negative charges.
How does hydrogen bonding occur in water?
Hydrogen bonding in water involves the electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to an electronegative atom (oxygen) and another electronegative atom (oxygen or nitrogen) in a neighboring molecule.