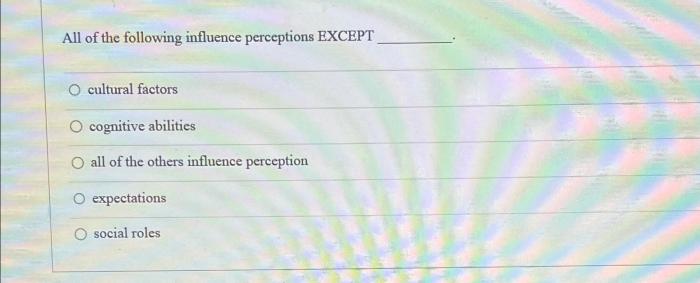
All of the following influence perceptions except: delves into the captivating realm of perception, where a myriad of factors shape our interpretations of the world around us. This exploration unveils the profound influence of cognitive, environmental, motivational, and physiological forces on our perceptions, while also shedding light on a notable exception.
As we delve deeper into this discourse, we will unravel the intricate interplay between these factors and their impact on our perceptions, ultimately gaining a comprehensive understanding of the forces that govern our subjective experiences.
Factors Influencing Perceptions

Perception is the process by which individuals interpret and give meaning to sensory information. Various factors influence perceptions, including cognitive, environmental, motivational, and physiological factors.
Cognitive Factors: All Of The Following Influence Perceptions Except
Cognitive factors refer to mental processes that influence how individuals perceive and interpret information.
Attention and Perception
Attention is the process of focusing on specific stimuli while ignoring others. Selective attention allows individuals to prioritize certain information, which can influence their perceptions.
Biases and Schemas
Biases are systematic errors in perception that can lead to distorted interpretations. Schemas are mental frameworks that organize and interpret information, which can also introduce biases.
Cognitive Dissonance
Cognitive dissonance refers to the psychological discomfort experienced when holding two or more conflicting beliefs or attitudes. This can lead individuals to seek information that supports their existing beliefs and avoid information that contradicts them.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors refer to external stimuli that influence perceptions.
Social and Cultural Context
Social and cultural norms, values, and expectations can shape how individuals perceive and interpret information.
Physical Surroundings and Sensory Stimuli
Physical surroundings, such as lighting, temperature, and noise, can influence perceptions. Sensory stimuli, such as colors, shapes, and sounds, can also affect how individuals interpret information.
Environmental Cues, All of the following influence perceptions except
Environmental cues, such as facial expressions, body language, and social cues, can provide information that influences perceptions.
Motivational Factors
Motivational factors refer to internal drives that influence how individuals perceive information.
Needs, Desires, and Goals
Individuals’ needs, desires, and goals can influence their perceptions. They may selectively attend to information that supports their goals and avoid information that conflicts with them.
Self-Serving Biases and Confirmation Bias
Self-serving biases lead individuals to attribute positive outcomes to themselves and negative outcomes to external factors. Confirmation bias leads individuals to seek information that supports their existing beliefs and avoid information that contradicts them.
Selective Attention and Interpretation
Motivations can lead individuals to selectively attend to and interpret information that aligns with their needs and goals.
Physiological Factors
Physiological factors refer to physical states that influence perceptions.
Physical Health, Sleep, and Substance Use
Physical health, sleep, and substance use can alter sensory processing and cognitive abilities, which can affect perceptions.
Physiological States
Physiological states, such as stress, anxiety, and hunger, can alter sensory processing and cognitive abilities, which can bias perceptions.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the primary factors that influence perceptions?
Cognitive factors (attention, biases, schemas, cognitive dissonance), environmental factors (social and cultural context, physical surroundings, sensory stimuli), motivational factors (needs, desires, goals, self-serving biases, confirmation bias), and physiological factors (physical health, sleep, substance use) are the key influencers of perception.
Can you provide an example of an exception to the factors that influence perceptions?
In certain instances, perceptions may not be influenced by all the aforementioned factors. For example, physiological factors may have a minimal impact on perception when an individual is in a state of heightened focus or deep concentration.