Chapter 6 review chemical bonding – Embarking on Chapter 6 Review: Chemical Bonding, we delve into the fascinating realm of the forces that govern the interactions between atoms. This exploration unveils the intricate tapestry of chemical bonding, a fundamental concept that underpins the very fabric of matter.
From the formation of simple molecules to the intricate structures of complex compounds, chemical bonding plays a pivotal role in shaping the properties and behavior of substances. As we unravel the complexities of ionic, covalent, metallic, and other types of bonding, we gain a deeper understanding of the chemical world around us.
Chemical Bonding Overview
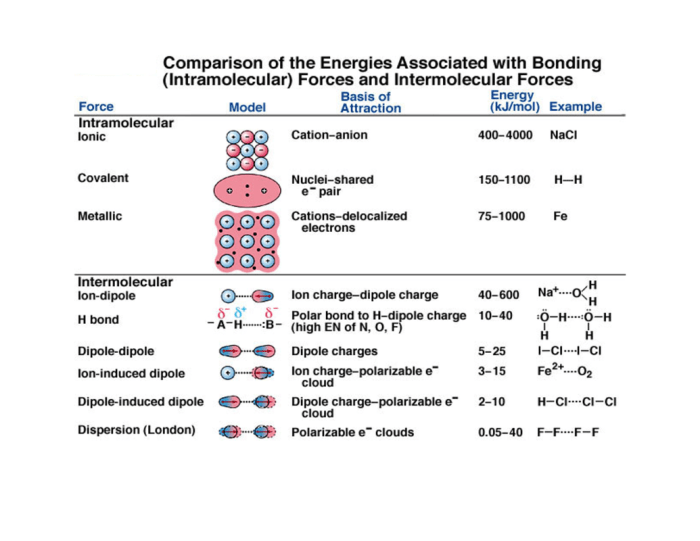
Chemical bonding refers to the forces that hold atoms together to form molecules and compounds. It determines the physical and chemical properties of substances. There are various types of chemical bonds, each with its own characteristics and properties.
Types of Chemical Bonds
- Ionic Bonding
- Covalent Bonding
- Metallic Bonding
Ionic Bonding
Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). These ions are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces, forming ionic compounds.
Properties of Ionic Compounds:
- High melting and boiling points
- Good electrical conductors in molten or aqueous solutions
- Brittle and hard
Examples:
- Sodium chloride (NaCl)
- Potassium fluoride (KF)
- Magnesium oxide (MgO)
Covalent Bonding
Covalent bonding occurs when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. The shared electrons form a covalent bond, which holds the atoms together.
Properties of Covalent Compounds:
- Lower melting and boiling points compared to ionic compounds
- Poor electrical conductors
- Can be gases, liquids, or solids
Examples:
- Water (H 2O)
- Methane (CH 4)
- Carbon dioxide (CO 2)
Metallic Bonding, Chapter 6 review chemical bonding
Metallic bonding is characterized by the sharing of electrons among a large number of metal atoms, forming a “sea of electrons.” This results in a strong, non-directional bond that holds the metal atoms together.
Properties of Metals:
- High electrical and thermal conductivity
- Shiny appearance (luster)
- Malleable and ductile
Examples:
- Iron (Fe)
- Copper (Cu)
- Gold (Au)
Helpful Answers: Chapter 6 Review Chemical Bonding
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the formation of charged ions, while covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms.
How does metallic bonding contribute to the properties of metals?
Metallic bonding involves the delocalization of electrons within a metal lattice, giving rise to high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and luster.
What factors influence the strength of chemical bonds?
Factors such as electronegativity, bond length, and bond order can significantly impact the strength of chemical bonds.