Improper earth ground on furnace – Improper earth grounding on furnaces poses a significant safety hazard, often overlooked but with potentially disastrous consequences. This comprehensive guide delves into the causes, effects, and essential troubleshooting techniques to ensure the proper grounding of your furnace, safeguarding your home and loved ones.
Understanding the importance of proper grounding is crucial. Without it, electrical faults can go undetected, leading to fires, shocks, and even electrocution. This guide provides step-by-step instructions on establishing a proper earth ground, identifying common signs of an improper ground, and taking the necessary safety precautions when working with electrical systems.
Improper Earth Ground on Furnace
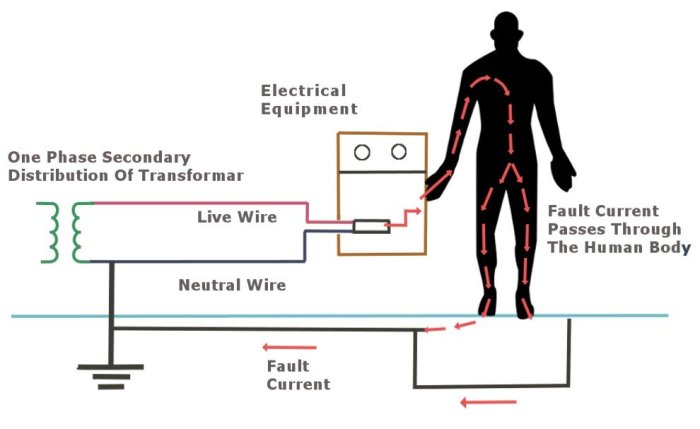
Proper grounding for furnaces is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the appliance. An improper earth ground can lead to a variety of potential consequences, including:
Electrical shocks
If the furnace is not properly grounded, it can become electrically charged. This can pose a significant risk of electrical shock to anyone who comes into contact with the furnace.
Fire hazards
An improper earth ground can also lead to fire hazards. If the furnace is not properly grounded, it can cause electrical arcing, which can ignite surrounding materials.
Damage to the furnace
An improper earth ground can also damage the furnace itself. Electrical arcing can cause damage to the furnace’s electrical components, which can lead to premature failure of the appliance.
Causes of Improper Earth Ground

Improper earth ground on furnaces can be caused by a variety of factors, including faulty wiring, corrosion, and loose connections.
Faulty wiring is a common cause of improper earth ground. If the wiring is not properly connected or if the insulation is damaged, it can create a path for electricity to flow outside of the intended circuit. This can cause the furnace to malfunction or even create a fire hazard.
Corrosion, Improper earth ground on furnace
Corrosion is another common cause of improper earth ground. When metal components are exposed to moisture, they can corrode and create a layer of rust. This rust can act as an insulator, preventing electricity from flowing properly through the ground wire.
As a result, the furnace may not be properly grounded and could pose a safety hazard.
Methods for Establishing Proper Earth Ground

Establishing a proper earth ground for a furnace is essential for ensuring safety and preventing electrical hazards. Here’s a detailed guide on how to establish an earth ground:
Materials Required:
- Earth ground rod (8 feet or longer)
- Ground clamp
- Ground wire (10 AWG or larger)
- Electrical tape
Step-by-Step Installation:
1.
-
-*Select a Grounding Location
Choose a location away from any buried pipes, cables, or other underground utilities.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
-*Drive the Earth Ground Rod
Drive the rod into the ground until the top is about 2 feet above the surface. Ensure it is driven straight into the ground.
-*Attach the Ground Clamp
Securely clamp the ground wire to the top of the earth ground rod using the ground clamp.
-*Run the Ground Wire
Route the ground wire from the earth ground rod to the furnace’s electrical panel.
-*Connect to the Furnace
Connect the ground wire to the furnace’s grounding terminal, typically located on the back or side of the unit.
-*Secure the Connections
Ensure all connections are tight and secure using electrical tape or other suitable methods.
Importance of Proper Grounding:
Proper grounding provides a safe path for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault, preventing shocks or fires. It also helps to stabilize the electrical system and reduce the risk of voltage fluctuations.By following these steps and using the correct materials, you can effectively establish a proper earth ground for your furnace, ensuring safety and preventing electrical hazards.
Troubleshooting Improper Earth Ground

An improper earth ground on a furnace can manifest in various ways. These include:
- Unusual humming or buzzing sounds emanating from the furnace
- Intermittent or flickering lights
- Malfunctioning electrical components
- Electric shocks when touching the furnace or its components
Identifying the Source of Improper Earth Ground
To troubleshoot an improper earth ground, follow these steps:
-
-*Inspect the ground wire
Ensure the ground wire is properly connected to the furnace’s chassis and to the electrical panel’s grounding bus.
-*Check the ground rod
If the furnace is grounded using a ground rod, inspect it for corrosion, damage, or loose connections.
-*Test the ground circuit
Using a multimeter, measure the resistance between the furnace’s chassis and the ground rod or grounding bus. A reading of 0 ohms indicates a proper ground.
Using a Multimeter to Test for Improper Earth Ground
To test for an improper earth ground using a multimeter:
- Set the multimeter to the ohms setting.
- Connect one probe to the furnace’s chassis and the other probe to the ground rod or grounding bus.
- Observe the reading on the multimeter. A reading of 0 ohms indicates a proper ground.
Safety Precautions

Working on electrical systems requires utmost caution and adherence to safety protocols. Ignoring safety measures can lead to severe electrical shocks, fires, or even fatalities.
Before commencing any work on a furnace, it is imperative to disconnect power to prevent accidental electrocution. Locate the electrical panel supplying power to the furnace and turn off the corresponding circuit breaker or fuse. Additionally, verify that the power is indeed disconnected using a non-contact voltage tester.
Dangers of Working on a Furnace with Improper Earth Ground
An improper earth ground on a furnace poses significant risks to both the equipment and individuals working on it. Without a proper earth ground, electrical current can flow through unintended paths, potentially damaging the furnace components or causing electrical fires.
Furthermore, an improper earth ground can create a hazardous situation for individuals working on the furnace. In the event of a fault, the lack of a proper earth ground can result in the accumulation of electrical charge on the furnace chassis, which can lead to electrical shocks or electrocution.
FAQ Corner: Improper Earth Ground On Furnace
What are the signs of an improper earth ground on a furnace?
Tingling or buzzing sensations when touching the furnace, flickering lights, or a burning smell are all potential signs of an improper earth ground.
How can I test for an improper earth ground on a furnace?
Using a multimeter, measure the voltage between the furnace frame and the earth ground rod. A reading of more than 1 volt indicates an improper ground.
What are the dangers of working on a furnace with an improper earth ground?
Working on a furnace with an improper earth ground can result in electrical shocks, burns, or even electrocution. Always ensure proper grounding before performing any electrical work.